 A table summarizing the factors which influence the financial forecasting frequency." width="1024" height="576" />
A table summarizing the factors which influence the financial forecasting frequency." width="1024" height="576" />Join over 2 million professionals who advanced their finance careers with 365. Learn from instructors who have worked at Morgan Stanley, HSBC, PwC, and Coca-Cola and master accounting, financial analysis, investment banking, financial modeling, and more.
Antoniya Baltova • 1 Apr 2024 • 7 min readFinancial forecasting helps stakeholders like investors, financiers, management, and others make informed decisions and manage financial risks. And while the process doesn’t eliminate uncertainty, it helps businesses plan and prepare for the future.
In a financial planning and analysis (FP&A) context, financial forecasting refers to the process of estimating and projecting future financial outcomes based on historical data, trends, and assumptions. It is a critical component of financial planning as it helps organizations anticipate and prepare for future scenarios.
The following article is an introduction to financial forecasting, which details the types, methods, and best practices. It’s intended for financial analysts, investors, and anyone looking to improve their financial planning and analysis skills.
Financial forecasting refers to the process of estimating a company’s future financial health by examining historical data provided by various financial disclosures, financial statements, and positioning statements (describing a company’s products or services and how they solve a particular problem in the target market). In addition, the process should consider the prevailing market conditions and historical financial trends.
The primary goal is to provide insights into future financial performance, allowing companies to make informed decisions and develop strategic plans. By analyzing past financial data, market trends, and other relevant factors, FP&A professionals can generate forecasts for key financial metrics, such as revenue, expenses, profits, cash flow, and balance sheet items.
Financial forecasting helps businesses in many ways, including:
Financial forecasting helps different stakeholders to make informed decisions—entrepreneurs and CEOs in terms of management, and external parties in terms of investments. Other applications and benefits include:
Financial plans can be divided into two groups: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative forecasts are suitable for businesses with a lot of historical data, while qualitative works better for companies with little historical data.
Quantitative forecasts can be used to project sales, variable, and fixed costs to determine a company’s growth. They are based on pro-forma financial statements—the Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement—with projected future financial data and assumptions based on past performance.
The following financial forecasting examples illustrate the process better.
Imagine that company X Inc. has the following expected performance figures for the next five years. You’re required to come up with a comparative financial statement for that period and evaluate the firm’s growth potential:
| Year | Sales | Operating Expenses | Non-Operating Expenses |
| 1 | 500,000 | 150,000 | 100,000 |
| 2 | 600,000 | 200,000 | 115,000 |
| 3 | 850,000 | 350,000 | 210,000 |
| 4 | 1,050,000 | 420,000 | 260,000 |
| 5 | 1,200,000 | 300,000 | 310,000 |
Cash sales are 60% of total sales, and cash expenses are 40% of the total amount for operating expenses and non-operating expenses. Assuming the company’s opening cash balance is 100,000, comment on X Inc.’s cash position.
Comparative Income Statement
 A table summarizing the factors which influence the financial forecasting frequency." width="1024" height="576" />
A table summarizing the factors which influence the financial forecasting frequency." width="1024" height="576" />
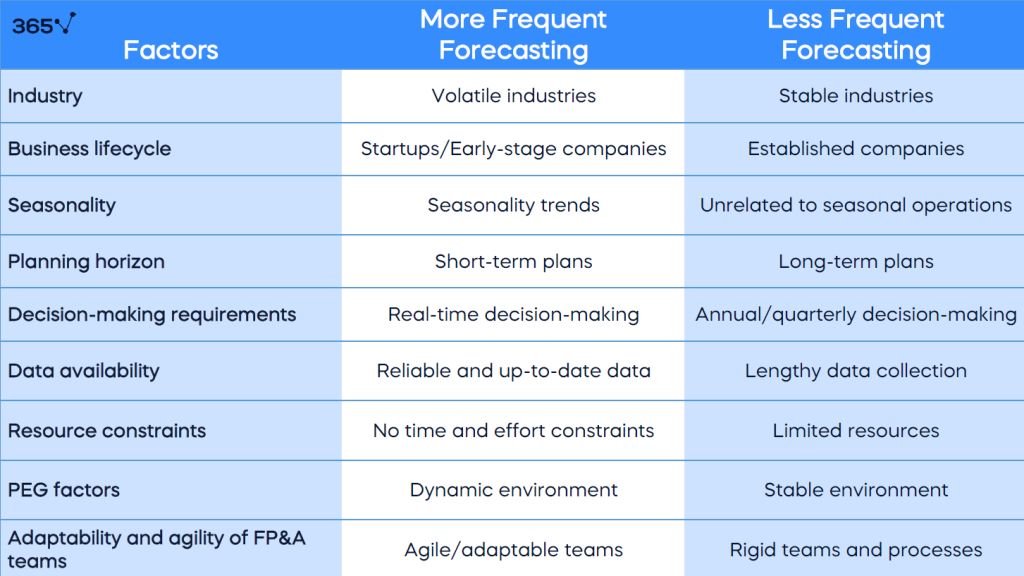
To sum up, organizations must assess their needs, objectives, and environment to determine the appropriate frequency of forecasting for their financial planning and analysis processes.
Financial forecasting is an essential part of FP&A, along with financial planning, budgeting, predicting performance, managing risk exposure, and other analytical activities that support decision-making.
If you wish to become a financial analyst, you need to master these skills. Our comprehensive FP&A: Building a Company’s Budget course covers everything you need to know. Sign up for free to try our learning program.
Financial forecasting methods can be quantitative or qualitative. The former includes calculating the percentage of sales, moving averages, simple and multiple linear regression models, etc. Common examples of qualitative forecasts are the Delphi technique and market research, among others. Learn more about them in the current article.
Financial forecasting vs budgetingA budget is a plan for a business’s operations with outlined goals and fixed spending limits. Meanwhile, a financial forecast includes expected outcomes and financial projections. While the former is useful as a short-term planning tool and rarely adjusted, the latter needs to be updated regularly and can be used to plan for the short and long term.
Financial forecasting vs financial modelingFinancial forecasting and financial modeling have distinct but complementary functions. Both processes are essential for a company’s financial planning. But while forecasting uses historical data to predict future performance, modeling relies on the information from these forecasts to simulate different scenarios and how they can impact expected performance. Thus, financial forecasting always precedes financial modeling.